In short (Architecture)
This article is meant to explain the architectural flow and flow event from client to data source and back.
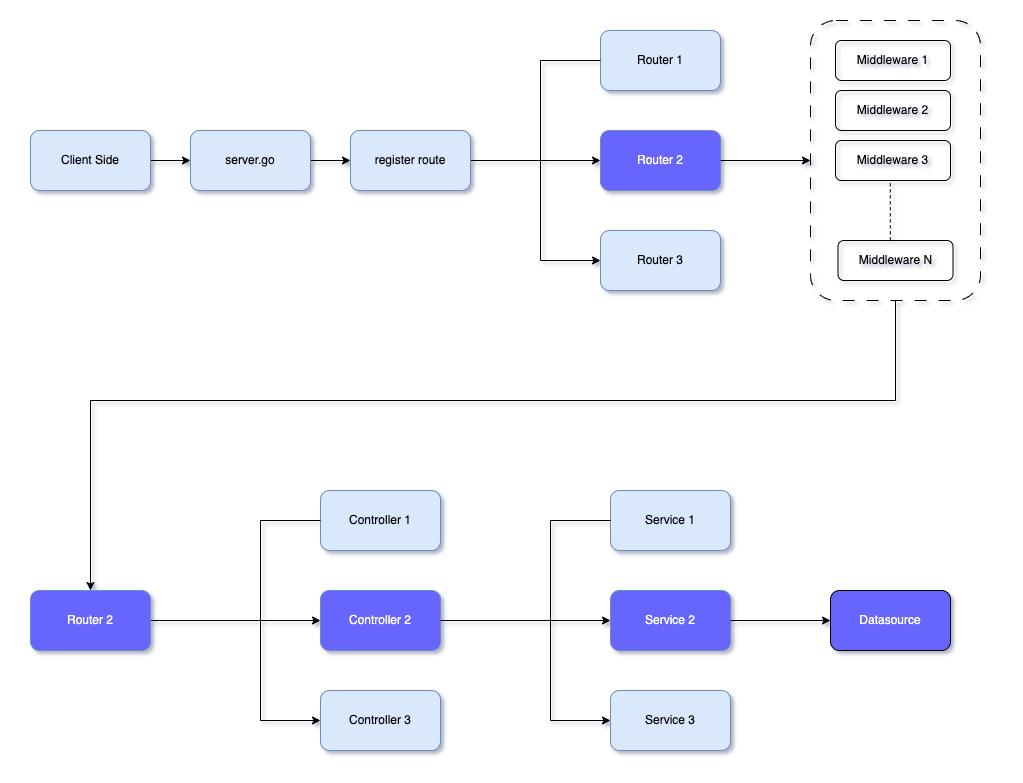
Architectural Flow Diagram
Main.go
The main.go is the entry point of the application.
// @title Niom-Sample
// @version 1.0
// @description Niom-Sample Backend REST API
// @in header
// @name Authorization
// @host 127.0.0.1:7000
// @BasePath /api
func main() {
// setup various configuration for app
config.LoadAllConfigs(".env")
server.Serve()
}
The comments above the main() is in Declarative Swagger Comments Format (DCF) you may read more about it here.
In short: Here we have done Swagger documentation for the API using annotations in the comments. The annotations start with the "@" symbol and provide information about the API's title, version, description, and authentication requirements. Specifically, the annotation "@in header" specifies that the authentication token should be provided in the header of the HTTP request.
config.LoadAllConfigs(".env")
Loads all the necessary configurations for the app using the "config" package's "LoadAllConfigs" function. LoadAllConfigs load configs from the .env file. The .env file must be in the current directory or you may specify a custom path as ./dir/prod/prod.env
server.Serve()
The main function calls the Serve method from the server package to start the server and begin listening for incoming requests on the specified host and base path.
Server Page
server/
┣ connecters.go
┣ middleware.go
┣ router.go
┗ server.go
Server.go
In server.go there is Serve function. The Serve function starts a Fiber server, registers middleware and routers, and listens for incoming requests on a specified port and host.
func Serve() {
appCfg := config.AppCfg()
// Define Fiber config & app.
fiberCfg := config.FiberConfig()
app := fiber.New(fiberCfg)
// other things
}
The function begins by loading the configuration for the app using the AppCfg and FiberConfig functions from the config package. Then initialize the server app to serve.
func Serve() {
// ....other codes
//initial the connecters
initConnectors()
//Attach Middleware
registerMiddleware(app)
registerRouters(app)
// ....other codes
}
The initConnectors() from connecter.go may use to initialize the app-level connector such as logger, database, etc. The registerMiddleware you may use to register global middleware here we have initialized API logger to monitor the request whereas registerRouters may use to register child router and router level middleware. Complete code can be here which is well commented for self-understanding.